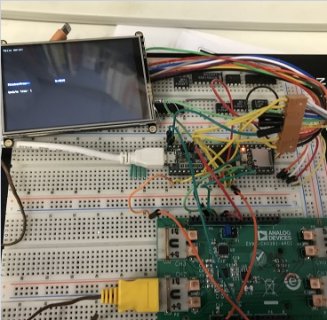
hello Tinkeres.
by using the flicker free library the flashing of the display goes away. however how do I prevent flickering if two programs are run after each other in the void loop?
ad7124 picks up data sends it away, closes the SPI bus,
hx8357 opens the spi bus and posts the data on the screen.
i crudely copied the codes to see if they work together, they do work,
but the flicker, anyway to circumvent this?
the speed is for ad7124 71ms.
Serial monitor code:
thanks for reading.
by using the flicker free library the flashing of the display goes away. however how do I prevent flickering if two programs are run after each other in the void loop?
ad7124 picks up data sends it away, closes the SPI bus,
hx8357 opens the spi bus and posts the data on the screen.
i crudely copied the codes to see if they work together, they do work,
but the flicker, anyway to circumvent this?
the speed is for ad7124 71ms.
Code:
#include <SPI.h>
#include <ad7124.h>
#include "Adafruit_GFX.h"
#include "HX8357_t3n.h"
#include <FlickerFreePrint.h> // library to draw w/o flicker
#define TFT_DC 9
#define TFT_CS 10
#define TFT_RST -1
#define AD7124_CS 8
#define AD7124_SPEED 5000000 // 2mhz?
Ad7124Chip strainADC;
#define TS_MINX 3800
#define TS_MAXX 100
#define TS_MINY 100
#define TS_MAXY 3750
#define C_BLACK 0x0000
#define C_BLUE 0x001F
#define C_RED 0xF800
#define C_GREEN 0x07E0
#define C_CYAN 0x07FF
#define C_MAGENTA 0xF81F
#define C_YELLOW 0xFFE0
#define C_WHITE 0xFFFF
HX8357_t3n tft = HX8357_t3n(TFT_CS, TFT_DC, TFT_RST);
FlickerFreePrint<HX8357_t3n> Data1(&tft, C_WHITE, C_BLACK);
FlickerFreePrint<HX8357_t3n> Data2(&tft, C_WHITE, C_BLACK);
unsigned long endmicros; //some global variables available anywhere in the program
unsigned long currentmicros;
const double Gain = 16;
const double Rf = 5.11E3;
const long Zero = 1L << 23;
const long FullScale = 1L << 24;
long SBraw[7];
double SBvolt[7];
long dataWord;
byte statusWord;
byte ch;
/* constants ================================================================ */
int filterWord = 100;
// Sample Speed Setting (Full Power Sinc3 Filter Mode)
// FW | SPS | SPS/Ch
// 600 | 6 | 1
// 100 | 60 | 10
// 40 | 156 | 26
// 20 | 300 | 50
float j;
unsigned long StartTime, EndTime;
char str[30];
SPISettings settingsAD7124(5000000, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE3);
SPISettings settingsTFT(25000000, LSBFIRST, SPI_MODE3);
#define TS_MINX 3800
#define TS_MAXX 100
#define TS_MINY 100
#define TS_MAXY 3750
/* public variables ========================================================= */
Ad7124Chip adc;
/* internal public functions ================================================ */
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setup() {
pinMode(AD7124_CS, OUTPUT);
pinMode(TFT_CS, OUTPUT);
SPI.begin();
//Initialize serial and wait for port to open:
Serial.begin (38400);
while (!Serial) {
; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for native USB port only
}
// prints title with ending line break
Serial.println ("AD7124 Voltmeter");
digitalWrite(AD7124_CS,LOW);
SPI.beginTransaction(settingsAD7124);
// Initializes the AD7124 device, the pin /CS is pin 10 (/SS)
// Initializes the AD7124 device, the pin /CS is pin 10 (/SS)
// Loop until ADC responds
int state = strainADC.begin(AD7124_CS);
while (state < 0) {
Serial.println(state);
Serial.println ("Failed");
delay(10);
state = strainADC.begin(AD7124_CS);
}
// Configuring ADC in Full Power Mode & Continuous Mode (Prevents sleep mode)
strainADC.setAdcControl(Ad7124::ContinuousMode, Ad7124::FullPower, true);
strainADC.setMode(Ad7124::ContinuousMode);
// Configure Channel 0
strainADC.setConfig(0, Ad7124::RefInternal, Ad7124::Pga1, true);
strainADC.setConfigFilter(0, Ad7124::Sinc3Filter, filterWord);
strainADC.setChannel(0, 0, Ad7124::AIN3Input, Ad7124::AIN2Input, true);
// Configure Channel 1
strainADC.setConfig(1, Ad7124::RefInternal, Ad7124::Pga1, true);
strainADC.setConfigFilter(1, Ad7124::Sinc3Filter, filterWord);
strainADC.setChannel(1, 1, Ad7124::AIN5Input, Ad7124::AIN4Input, true);
// Configure Channel 2
strainADC.setConfig(2, Ad7124::RefInternal, Ad7124::Pga1, true);
strainADC.setConfigFilter(2, Ad7124::Sinc3Filter, filterWord);
strainADC.setChannel(2, 2, Ad7124::AIN7Input, Ad7124::AIN6Input, true);
// Configure Channel 3
strainADC.setConfig(3, Ad7124::RefInternal, Ad7124::Pga1, true);
strainADC.setConfigFilter(3, Ad7124::Sinc3Filter, filterWord);
strainADC.setChannel(3, 3, Ad7124::AIN9Input, Ad7124::AIN8Input, true);
// Configure Channel 4
strainADC.setConfig(4, Ad7124::RefInternal, Ad7124::Pga1, true);
strainADC.setConfigFilter(4, Ad7124::Sinc3Filter, filterWord);
strainADC.setChannel(4, 4, Ad7124::AIN11Input, Ad7124::AIN10Input, true);
// Configure Channel 5
strainADC.setConfig(5, Ad7124::RefInternal, Ad7124::Pga1, true);
strainADC.setConfigFilter(5, Ad7124::Sinc3Filter, filterWord);
strainADC.setChannel(5, 5, Ad7124::AIN13Input, Ad7124::AIN12Input, true);
strainADC.enableChannel(0,true);
strainADC.enableChannel(1,true);
strainADC.enableChannel(2,true);
strainADC.enableChannel(3,true);
strainADC.enableChannel(4,true);
strainADC.enableChannel(5,true);
strainADC.enableChannel(6,false);
strainADC.enableChannel(7,false);
delay(100);
digitalWrite (AD7124_CS, HIGH);// setting the CS Pin high
SPI.endTransaction();
SPI.beginTransaction(settingsTFT);
digitalWrite(TFT_CS,LOW);
tft.begin();
tft.begin();
tft.setRotation(1);
tft.fillScreen(C_BLACK);
tft.fillRect(0, 0, 319, 35, C_RED);
tft.fillRect(0, 130, 319, 35, C_BLUE);
SPI.endTransaction();
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
void loop()
{
// get some data
currentmicros = micros();
digitalWrite(AD7124_CS,LOW);
SPI.beginTransaction(settingsAD7124);
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++)
{
strainADC.waitEndOfConversion(100);
dataWord = strainADC.getData();
ch = strainADC.currentChannel();
// check RDY bit
if (ch >= 0) {
SBraw[ch + 1] = dataWord;
SBvolt[ch] = Ad7124Chip::toVoltage(SBraw[ch], 1, 2.5, true);
}
}
Serial.print("$");
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(SBvolt[i]);
}
Serial.print(" || ");
Serial.print(currentmicros);
Serial.print(" || ");
Serial.print(micros());
Serial.print(" || ");
unsigned long endmicros=currentmicros-micros();
Serial.print(endmicros);
Serial.print(" usec");
Serial.println("");
SPI.endTransaction();
SPI.beginTransaction(settingsTFT);
digitalWrite(TFT_CS,LOW);
tft.fillScreen(HX8357_BLACK);
tft.setTextColor(HX8357_WHITE); tft.setTextSize(1);
tft.setCursor(0, 0);
tft.println("Hello World!");
///----- flicker test
j += 0.0013;
// now let's see the tft update with FlickerFree
tft.setCursor(10, 140);
tft.setTextColor(C_WHITE, C_BLUE);
tft.print("FlickerFree: ");
// set cursor as you would normall do
tft.setCursor(180, 140);
// you must call the text colors for the object
Data1.setTextColor(C_WHITE, C_BLUE);
StartTime = millis();
// one call and flicker free paint is done
Data1.print(j, 4);
// lets see how fast
EndTime = millis() - StartTime;
tft.setTextColor(C_WHITE, C_BLACK);
tft.setCursor(10, 170);
sprintf(str, "Update time: %lu", EndTime);
tft.setCursor(10, 170);
Data2.setTextColor(C_WHITE, C_BLACK);
Data2.print(str);
digitalWrite(TFT_CS,HIGH);
SPI.endTransaction();
}Serial monitor code:
Code:
AD7124 Voltmeter
_t3n::begin mosi:11 miso:12 SCLK:13 CS:10 DC:9 SPI clocks: 26000000 2000000
_t3n::begin - completed
_t3n::begin mosi:11 miso:12 SCLK:13 CS:10 DC:9 SPI clocks: 26000000 2000000
_t3n::begin - completed
$,-2.50,-0.00,-0.00,0.85,1.39,0.00 || 2402671 || 2478261 || 4294891703 usecthanks for reading.